Categories
- Wire & Cable
- Multi-conductor & Signal Cable
- Battery Cable Assemblies
- Terminals and Connectors
- Electrical Parts
- Electrical Tools
- ID Products
- Wire Management
- Tape & Sealant
- Mounting Panels & Panel Blanks

Need Help?
Click HereGet a Business Account
Apply HereMulti-conductor


What is multi-conductor cable?
Multiconductor is a term used to describe a wire or cable that carries more than one internal conductor. That means there is an insulated conductor within an outer insulated jacket. Usually, multiconductor cable has between two and twenty-five conductors, although some cables are designed for specific purposes and can far exceed that number. The term multiconductor is a generalized term that can refer to a wide range of cables; however, this page is dedicated to the most common type of multiconductor cable available: shielded and unshielded. Multiconductor cables are commonly used for control purposes. Things such as remote signaling, communications, and broadcast applications, to name a few. These cables are manufactured to meet the latest UL, CSA, and NEC requirements. Now that we have a basic understanding of what we mean by multiconductor, let’s take a look at the two main types you’ll find.
"Multiconductor cables are commonly used for control purposes. Things such as remote signaling, communications, and broadcast applications, to name a few."
What is the difference between shielded and unshielded multi-conductor cables?
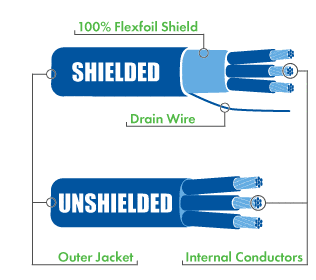
The most obvious difference is the addition of a foil shield on the cable or the absence of that foil shield, but it goes further than that. The foil shield is used in environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is an issue. Say, for instance, that you need to run cables through an industrial or factory setting where there is high-powered equipment in operation. That equipment may transmit electromagnetic frequencies that would interrupt or interfere with the signal passing through the multi-conductor cable. By using a shielded multi-conductor cable, you eliminate the risk of electromagnetic interference (EMI). Each shielded cable comes with a drain wire that terminates and grounds the entire shield, which in turn makes it more efficient. So why would you use an unshielded multi-conductor cable? In situations where no electromagnetic interference (EMI) is present, the shield is not required and, in all honesty, unnecessary. The best course of action is to use the best-suited cable for the task at hand.
What benefits does each type of multi-conductor cable offer?
Unshielded multi-conductor cable offers the benefits of being easier to work with and being less expensive. That means that you can install this cable quicker and cheaper than shielded multi-conductor cable. On the other hand, shielded multi-conductor cable offers a higher level of protection, specifically from electromagnetic interference (EMI), but takes a few extra steps to install. With that being said, they both offer some consistent benefits.
Both offer high-quality, durable interior conductors that are made from tinned copper, reducing your chances of dealing with a corroded wire. Additionally, both styles carry durable yet flexible insulation as well as a durable exterior jacket. This means that these cables were designed for demanding environments. These aren’t your everyday multi-conductor cables; these were made to stand up to harsh conditions for an extended period of time.
![]()
Flexible
![]()
Durable
![]()
High-quality
Are multi-conductor cables protected against the marine environment?
The marine environment is unforgiving, which is why we ensured that both the shielded multi-conductor cable and the unshielded multi-conductor cable we offer are built to handle the toughest marine conditions. They carry two layers of high-quality, durable PVC insulation. This serves to protect the wires while making them easier to route at the same time due to their flexibility. These cables are used in more than just the marine environment, as they can be found in multiple types of industrial applications. The point is that the multi-conductor cables we offer are designed to last. To ensure their longevity, use approved terminals and cover any exposed conductor area with epoxy-lined heat shrink.
![]()
Where is multi-conductor cable implemented?
![]()
Prepped examples of shielded and unshielded cable
Shielded and unshielded multi-conductor cables are implemented in applications that require multiple conductors, often where protection from electromagnetic interference (EMI) is required. They are utilized in new wire installations and as replacement cables when performing maintenance. How do you know if it's time to replace them? The biggest indicator that it is time to replace your multi-conductor cables would be external damage. Is the insulation faded, chipped, or burnt? Is there cracked insulation? If so, it is time to install a new multi-conductor cable. All you need is the proper tools as well as the proper terminals and connectors.
Where would you use shielded multi-conductor cable?

Shielded multi-conductor cable is ideal for situations where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is an issue. They are built to protect against EMI and transmit signals unimpeded. They are a solid choice where a durable, yet flexible cable is needed to handle a tough environment. Pacer's shielded multi-conductor cables are flexible, which is extremely beneficial for applications where cables are run through trays or across facilities where there are turns, bends, and exposure to vibration. So, you would use Pacer shielded multi-conductor cable in situations that call for durability, flexibility, longevity, and resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI).
"They are a solid choice for industrial or electronic facilities where a durable, yet flexible cable is needed to handle a tough environment."
Where would you use unshielded multi-conductor cable?

Unshielded multi-conductor cables are ideal for use in applications that require a cable to be tough and flexible while carrying multiple conductors in a protective jacket. Remember, these cables do not offer the electromagnetic interference protection that you get with the shielded cables, but not every situation calls for those. Whether you’re looking for multi-conductor cables for use in a factory, industrial setting, or a boat, these cables are a solid choice for the level of longevity they offer. If they are tough enough for industrial settings, then you know they can easily handle marine applications.
What gauges are available?
Pacer carries both shielded multi-conductor cables and unshielded multi-conductor cables in a range of gauge sizes to handle a variety of applications. Currently, we offer both styles in 14-gauge, 16-gauge, 18-gauge, 20-gauge, and 22-gauge sizes as they are the most commonly required for marine use. Looking for another size that isn’t listed here? Contact a Pacer expert today and see what other solutions we have to offer.
![]()
14 AWG
Unshielded
![]()
16 AWG
Shielded
![]()
18 AWG
Unshielded
![]()
20 AWG
Shielded
![]()
22 AWG
Unshielded
How many conductors are available?
Pacer offers multi-conductor cables with anywhere from two to twenty-five conductors. The number of conductors available is dependent on two factors. The first factor is whether you choose shielded or unshielded multi-conductor cable. Each style carries a different number of conductors as their intended uses are different. The second factor is the gauge size you have chosen. The general rule is that the smaller the wire gauge, the more conductors are potentially available. So, where a 14-gauge multi-conductor cable may only offer three or four conductors, a 22-gauge multi-conductor cable can carry up to twenty-five conductors.
"Each style carries a different number of conductors as their intended uses are different."
| Wire Gauge | # of Conductors-Unshielded | # of Conductors-Shielded |
|---|---|---|
| 14AWG | 2 | 2, 3 |
| 16AWG | 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 12 | 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 |
| 18AWG | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12 | 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15 |
| 20AWG | 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 15 | 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15 |
| 22AWG | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 15, 25 | 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10 |
What compliances does multi-conductor cable meet?
Pacer strives to manufacture or carry only the highest quality cables that meet a host of compliances. Below you will find a list of the compliances that Pacer shielded multi-conductor cable and unshielded multi-conductor cable meet or exceed. Click on any of the links to be taken directly to that compliance.
What industries use multi-conductor cable?
Multi-conductor cable is utilized by a wide range of industries due to its durability, flexibility, and longevity. You will commonly find multi-conductor cables, both shielded and unshielded, in such industries as signal transmission, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment. The fact that these cables are so common is a testament to how useful they are. They are used in marinas, repair shops, industrial job sites, and even private boats. They are ideal for industrial, commercial, and marine applications.
*This page was updated on 1/30/2025*






