Click on the image of the chart you are interested in to learn more about that topic.
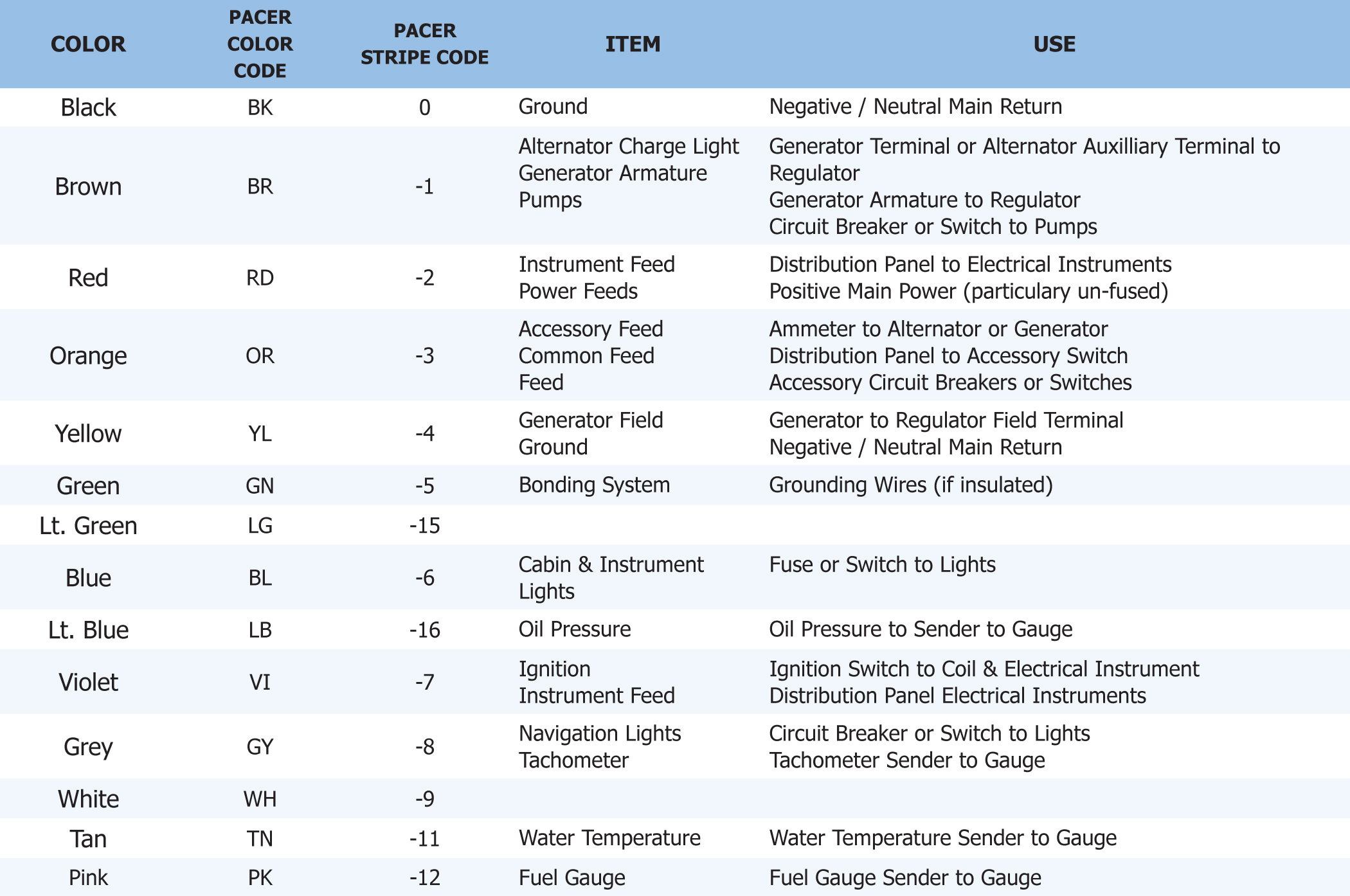
ABYC COLOR CODES - The American Boat and Yacht Council have set standards designed to simplify the wiring process as well as making repairs and wire replacement easier. By using specific colors for specific equipment, the troubleshooting process becomes much simpler. Using this chart you can quickly identify which wires run to each piece of equipment.
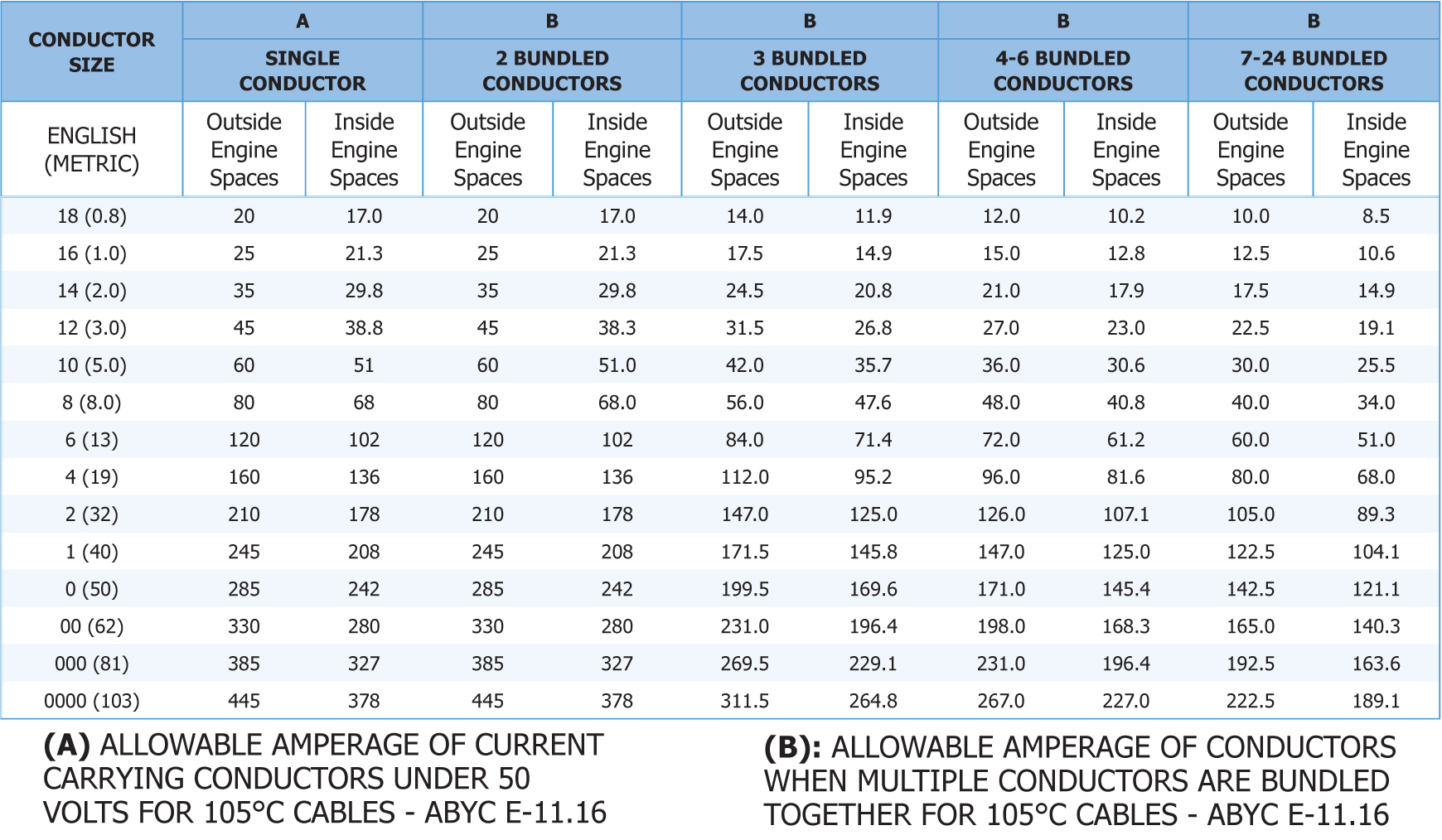
ALLOWABLE AMPERAGE OF CONDUCTORS - Using this chart will allow you to quickly and easily determine the current carrying capacity for your wires and cables. All you will need to know is, the gauge of your wire or cable, the number of conductors bundled together and whether or not the wires will be inside or outside of the engine bay. It's that simple.
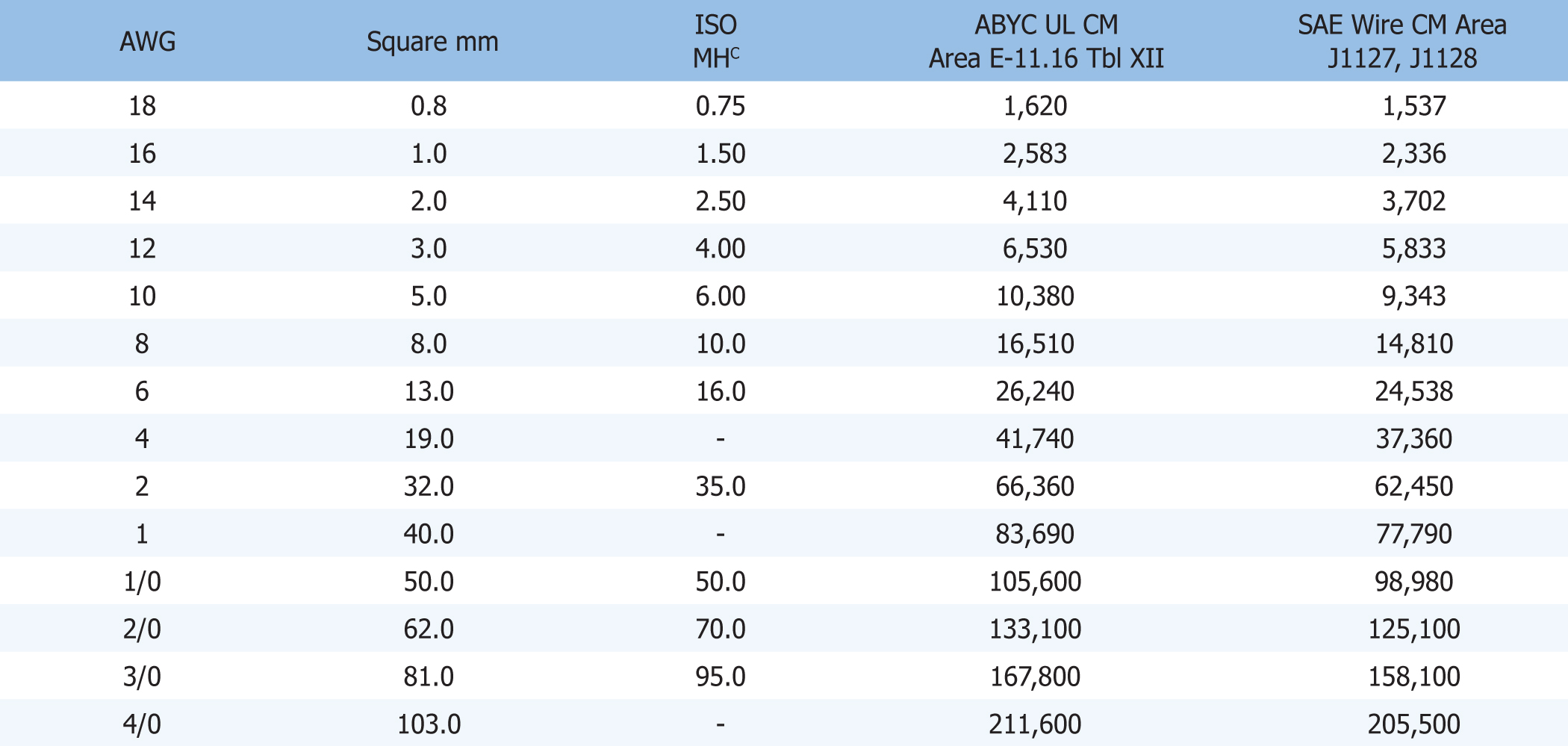
CONDUCTOR CIRCULAR MIL (CM) AREA - Circular mil area is a unit of measure that is equal to the area of a circle with a diameter of one mil (1/1000 of an inch). One advantage of using circular mils is that it can be calculated without reference to Pi (3.14). This unit makes conversion between cross section and diameter of a wire much easier than other methods. The chart on the left can be used to quickly determine the circular mil area of a given gauge.
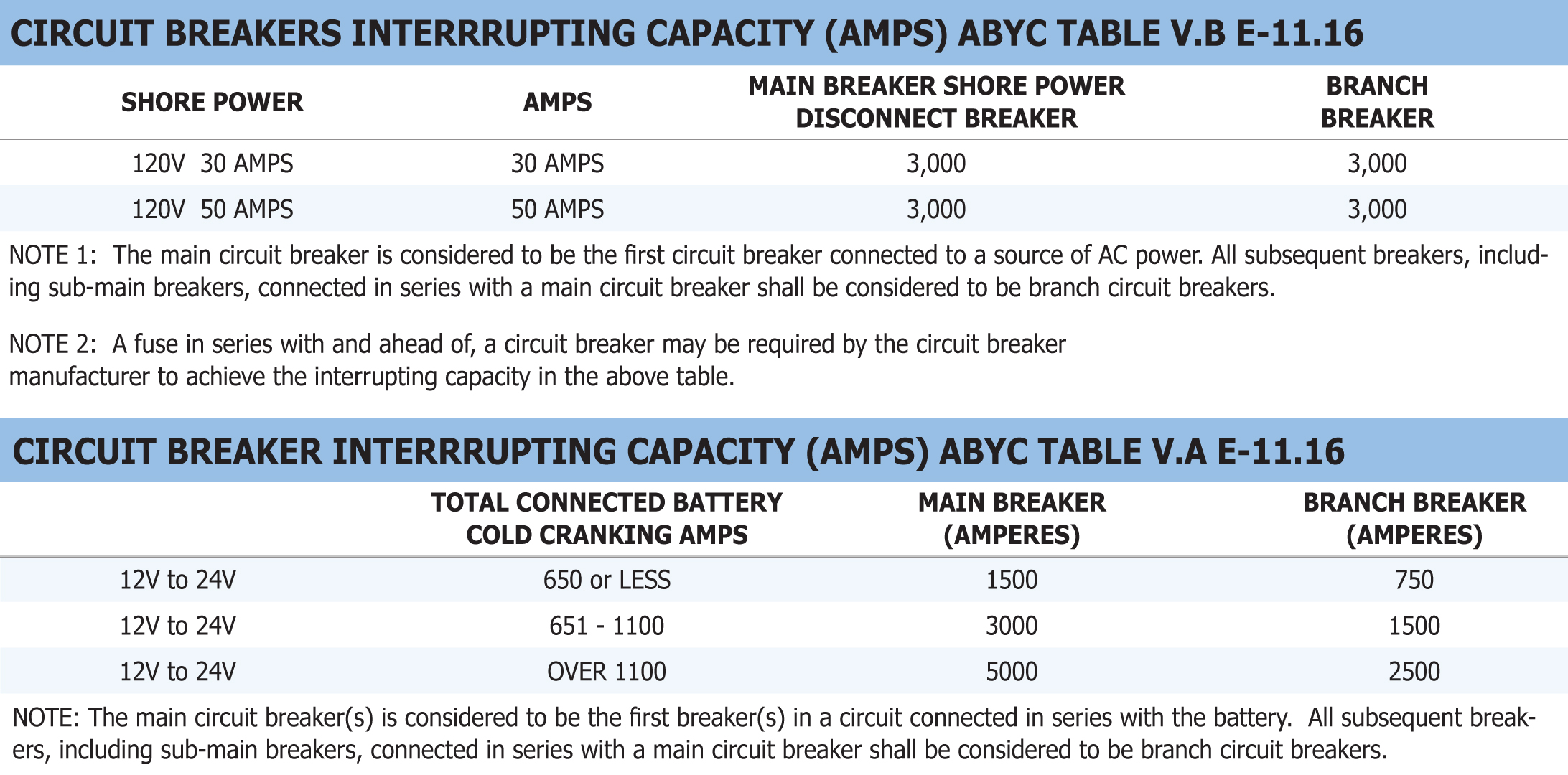
CIRCUIT BREAKER INTERRUPTING CAPACITY - Interrupting capacity, or breaking capacity rating is the current a circuit breaker, fuse, or other electrical device can "interrupt" without sustaining damage or being destroyed. This chart can be used to help gain a better understanding.
VOLTAGE DROP CALCULATOR - All wire has a finite resistance to current flow. This resistance causes voltage to develop across the length of a current carrying conductor. The result is that the intended load is robbed of the full potential of it's battery source. The chart to the left is designed to help you determine voltage drop at either 12 volt or 24 volt and can be used to calculate 3% or 10% drop.
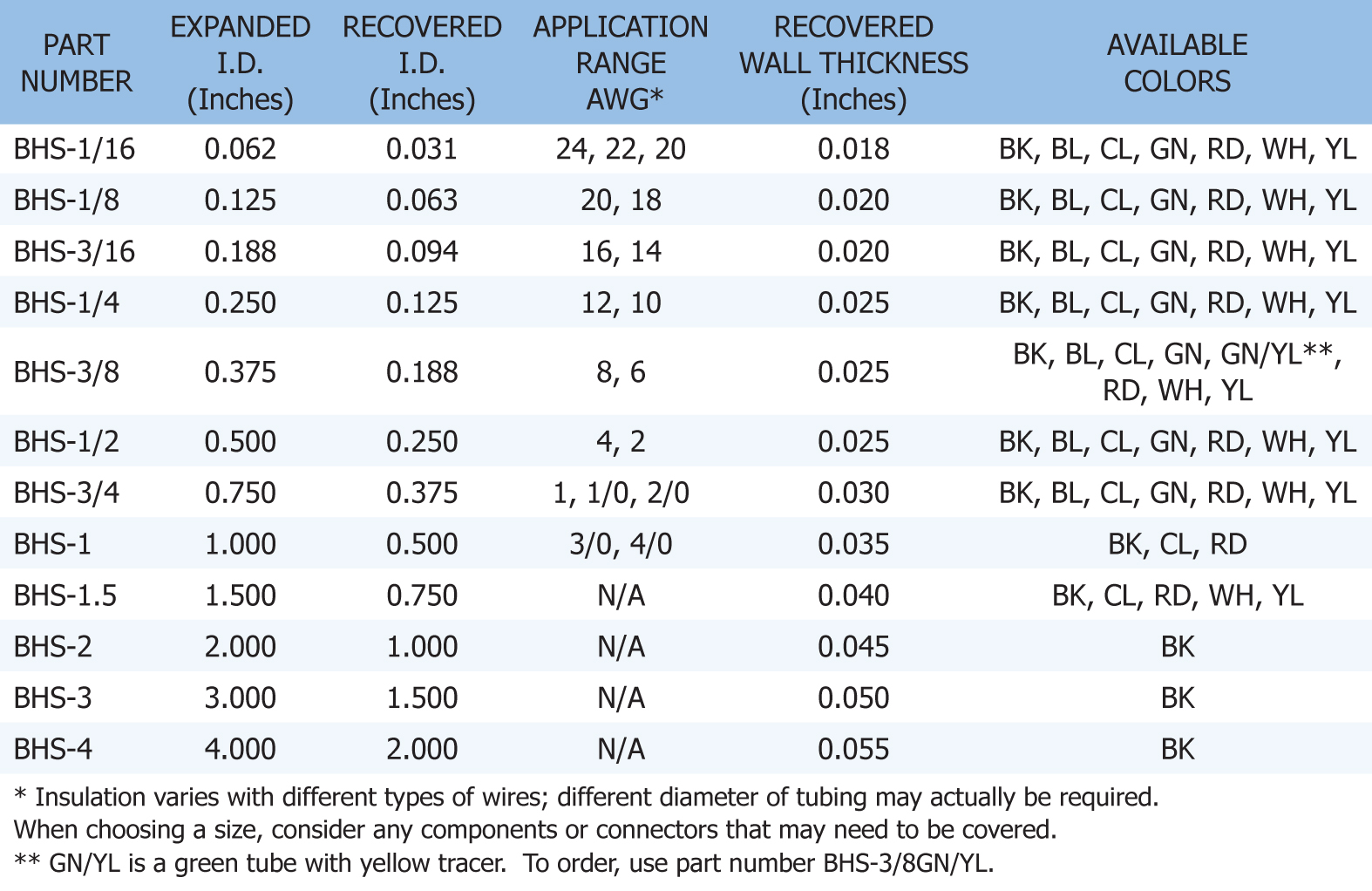
2-to-1 HEAT SHRINK TUBING - Two-to-one heat shrink tubing slides easily over small inline splices and connectors, and shrinks down to 50% of it's original diameter to fit snugly over any wire, hose or cable. Also, it is the ideal way to terminate the ends of your braided sleeving and create a tight professional look. This chart will give you an understanding of the tubing and help you to select the correct size for your current task.
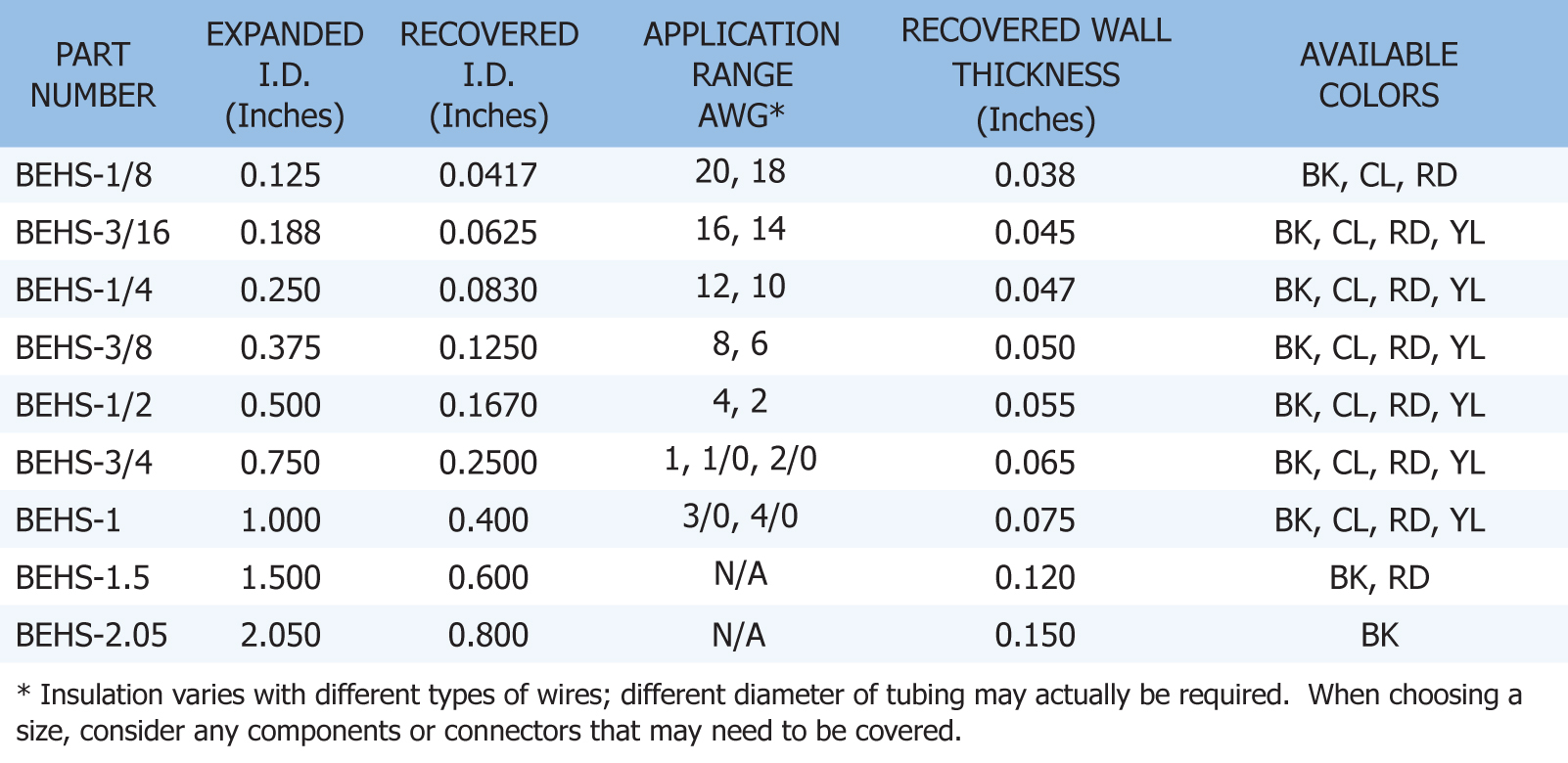
3-TO-1 ADHESIVE LINED HEAT SHRINK - Three-to-one heat shrink is a semi-flexible, cross linked tube which possesses a meltable inner lining of adhesive that flows when heated. This ensures complete sealing. In additional to insulation and mechanical protection, it also provides a moisture proof barrier for encapsulating wires, splices, breakouts and components. This chart will help you to decide which size you need.
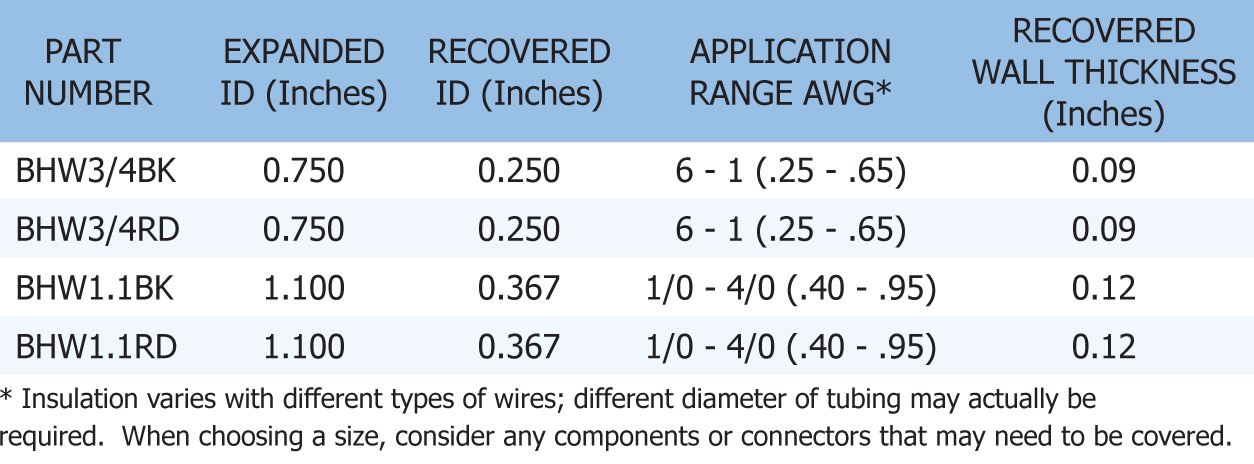
HEAVY WALL TUBING - Heavy wall tubing is internally coated with a dual purpose thermoplastic liner, which flows and encapsulates when heated. When cooled, the tubing offers the mechanical strength of a superior adhesive and the corrosion protection of a high quality mastic. When choosing a size, consider any components or connectors that may need to be covered. This chart will help you to select the correct size for the project you're working on.